
What is NFC?
Near Field Communication (NFC) is a short range radio technology which is based on RFID(radio-frequency identification) and enables communication between devices that either touch or are momentarily held close together, usually not more than a few centimeters.NFC is an open-platform technology,standardized in the NFC Forum and supports different data transmission rates such as 106 kbps, 212 kbps, and 424 kbps.It sets up faster than Bluetooth.Communication is also possible between an NFC device and an unpowered NFC chip, called a “tag”.
NFC tag, Reader, Operating modes etc...
Tag and Reader
NFC-based communication between two devices is possible when one device acts as a reader/writer and the other as a tag.
Tag: The tag is a thin simple device containing antenna and small amount of memory. It is a passive device, powered by magnetic field. Depending on the tag type the memory can be read only, re-writable, and writable once.
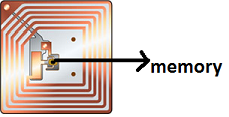
Reader: The reader is an active device, which generates radio signals to communicate with the tags. The reader powers the passive device in case of passive mode of communication.
NFC Modes
Communication modes:NFC devices support two communication modes.
Active: In this mode, the target and the initiator devices have power supplies and can communicate with one another by alternate signal transmission.
Passive: In this mode, the initiator device generates radio signals and the target device gets powered by this electromagnetic field. The target device responds to the initiator by modulating the existing electromagnetic field.
Operating Modes: NFC devices can operate in three different modes based on the ISO/IEC 18092, NFC IP-1 and ISO/IEC 14443 contactless smart card standards.
Read/Write: In this mode, the NFC enabled phone can read or write data to any of the supported tag types in a standard NFC data format.
Peer to Peer: In this mode, two NFC-enabled devices can exchange data. For example, you can share Bluetooth or Wi-Fi link set up parameters to initiate a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi link. You can also exchange data such as virtual business cards or digital photos. Peer-to-Peer mode is standardised on the ISO/IEC 18092 standard.Note: The Symbian implementation for NFC currently supports initiation of Bluetooth link, while Wi-Fi is not supported yet. Also, the Java implementation for NFC does not support this mode of operation.
Card Emulation: An NFC-enabled phone acts as reader when in contact with tags. In this mode, the phone can act as a tag or contactless card for existing readers.Introduction to NFC 8 Note: The Symbian and Java implementation for NFC does not currently support this mode of operation.
Present and anticipated applications:(The use cases and possibilities are beyond imagination)
- Contactless transactions -Payment ( An NFC-enabled phone can be used in a payment application like a credit card to make payments. To pay, the user must touch the payment terminal with the phone. The NFC-enabled phone acts as a contactless card (chip based credit card) to the payment terminal (reader).)
- Data exchange – Sharing (Two NFC enabled devices can share business card information, contacts, files etc..The information is shared in the NFC data format recognized by both devices.)
- Service initiation – Smart poster is an example of service initiation where NFC tags are placed behind the movie poster under each hot spot. Each tag contains a piece of data in the NFC data format known as smart poster. When an NFC enabled phone touches a tag (or hot spot) in the poster, information in the tag is read by the phone. Depending on the type of information read, the NFC phone may start a video stream, open a web browser, or ask the user if he wants to place a telephone call.
- Ticketing- An NFC enabled device or phone can replace a travel card or ticket.User can refill the tickets by paying and touching the ticketing machine.
- Simplified setup of more complex communications such as Wi-fi.
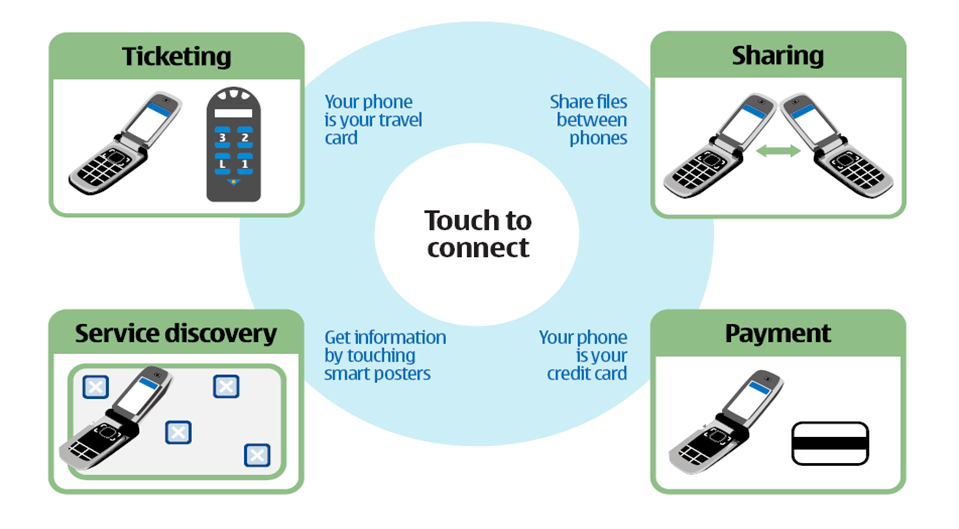
The other uses are printing from your camera by bringing it closer to printer, getting into bus by waving your NFC enabled phone, setting up wireless home office with a touch and secure payment etc..,
- 130+ leading NFC companies working together to advance the use of NFC technology.
-
By 2013, every three in five phones will have NFC. (Source: Juniper Research)
- The gross transaction value made via NFC will exceed $75 billion globally by 2013.
- NFC is simple and safe,speed, very intuitive and flexible with Frequency-13.56 MHz and Transfer rate-424 kbps.
 We will roll out one more article on NFC forum,certification, ecosystem and building NFC based applications.
We will roll out one more article on NFC forum,certification, ecosystem and building NFC based applications.
So the conclusion is that NFC is on solid ground.The foundation has been laid for enormous growth.They are inventing the future!Possibilities are as wide as imagination.
 Spinfold VisualDictionary-Evolutree- Technorip-Amazing Facts and much more.
Spinfold VisualDictionary-Evolutree- Technorip-Amazing Facts and much more.





